Description
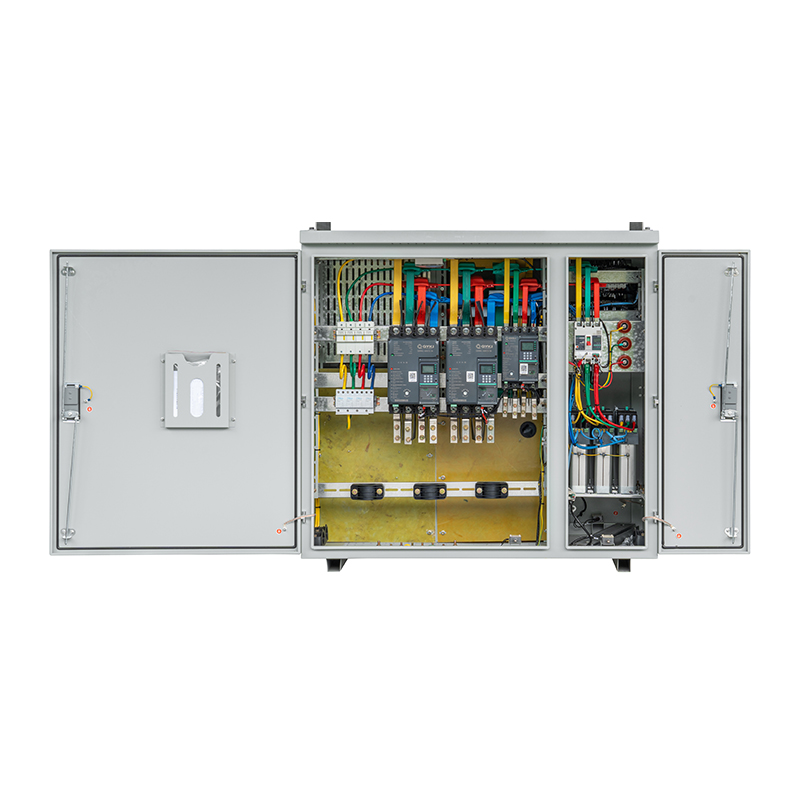
The JP Cabinet is an AC low-voltage metering distribution box widely used in rural power grids, residential communities, and other low-voltage distribution systems. It integrates functions for power conversion, distribution, control, and metering in one compact enclosure.
2. Key Features
- Compact Design – Modular structure integrates multiple electrical devices into a single cabinet, saving space.
- High Protection Level – IP54 or higher, suitable for various outdoor environments.
- Easy Operation – Flexible door opening and well-organized internal layout for convenient maintenance.
- Safety & Reliability – Equipped with overcurrent, overvoltage, leakage, and other protection functions.
3. Technical Specifications
- Rated Voltage: AC 380V/220V (Three-phase four-wire)
- Rated Frequency: 50Hz
- Rated Current: 100A – 630A (depending on model)
- Short-Circuit Withstand Current: 10kA – 50kA, 1–3 seconds
- Protection Level: IP54
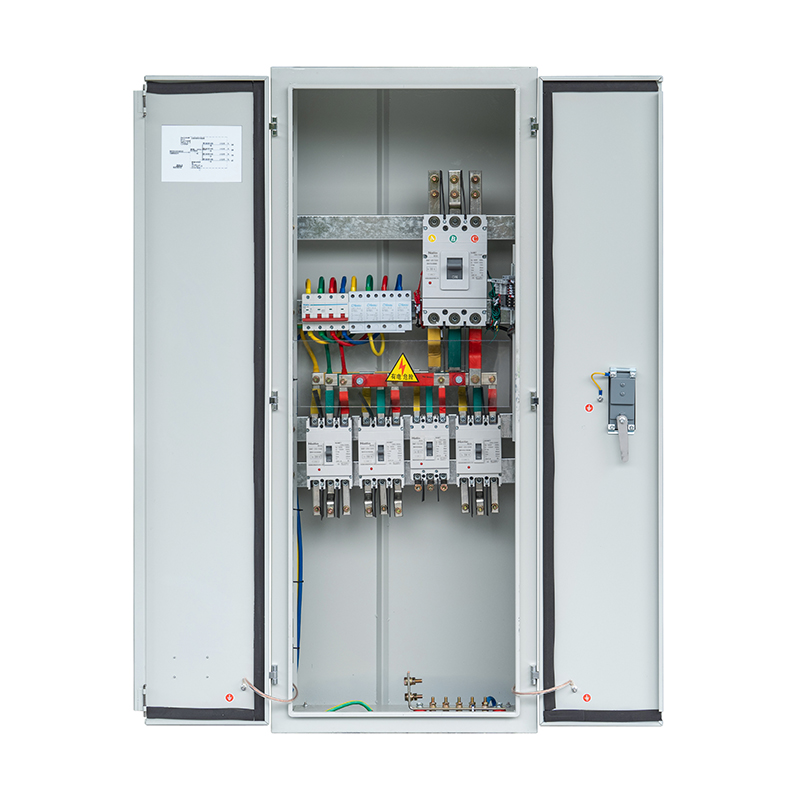
4. Main Components
- Cabinet Body – High-quality cold-rolled steel, corrosion-resistant coating, with front door observation window.
- Busbar System – Copper or aluminum main and branch busbars sized per current rating.
- Circuit Breakers – Molded case or miniature type, with overload and short-circuit protection.
- Fuses – Backup short-circuit protection.
- Contactors – For motor load control, supporting remote or automatic operation.
- Metering Devices – Energy meter, current transformers for power measurement.
- Protection Devices – Leakage, overvoltage, and undervoltage protection units.
- Secondary Circuit – Control, protection, and signaling devices such as switches, lamps, and relays.
5. Installation & Commissioning
- Install in a dry, well-ventilated environment, away from corrosive gases and flammable materials.
- Ensure a level, firm foundation, and adequate clearance for operation.
- Secure cabinet to base channel steel with bolts, connect busbars and wiring as per markings.
- Perform insulation resistance tests, withstand voltage tests, and protection device checks before energizing.
6. Operation
- Closing: Check equipment status → close main breaker → close branch breakers.
- Opening: Open branch breakers → open main breaker.
- Avoid operating under heavy load and follow safety procedures.
7. Maintenance
- Routine: Clean surface, check door seals, tighten connections, and inspect for abnormal heat or noise.
- Periodic: Inspect breakers, fuses, busbars, and protective devices every 6–12 months.
8. Transport & Storage
- Avoid strong vibrations and impacts; use proper packaging such as wooden crates.
- Store upright in a dry, ventilated place; inspect periodically during storage.
Request a Quote Now
Our team will get back to you within 24 hours.